Indexing means selecting a subset of elements from the matrix. Most of us are familiar with numerical indexing used to read or write specific Matrix elements. MATLAB provide logical indexing for quick matrix operations. Check the playlist to learn about MATLAB.
Let’s see what logical indexing is and how we can eliminate program loops using logical indexing.
What is Logical Indexing?
Logical operators such as less than (<), greater than (>), equal to (==), and not equal to (~=); perform a comparison between two values. The outcome of the comparison is either true(1) or false(0).

What happens if we compare a vector or a matrix to a single scalar?

The result is an array of ones and zeros of the same size as the original array, which is also called a logical array.
We can use a logical array as an array index where MATLAB extracts the array elements where the index is true. We can use a logical array as an index to re-assign values in an array.
Logical Indexing Examples
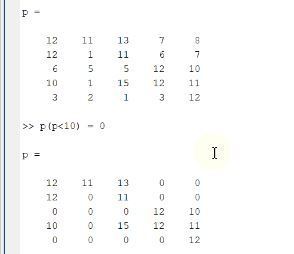
Let’s create a matrix of random numbers. Check our article here to learn more on vectors and matrices. We want to find values less than 10 and replace them with zero. We can do it in one statement using the logical index.
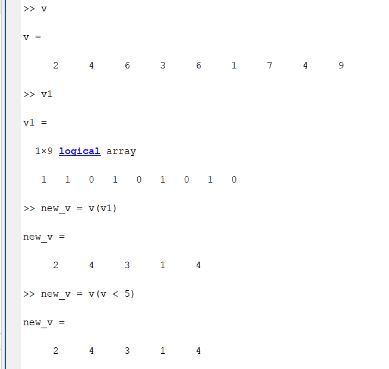
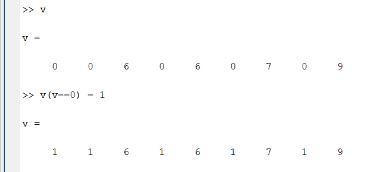
We have a row vector v of nine elements. We want to find and replace values less than 5. One way to do this is the use of the ‘for’ loop and the ‘if’ construct.

The other way is to use logical indexing.
Access data in Tables using Logical Indexing
Let’s import population data from an excel file into a table.
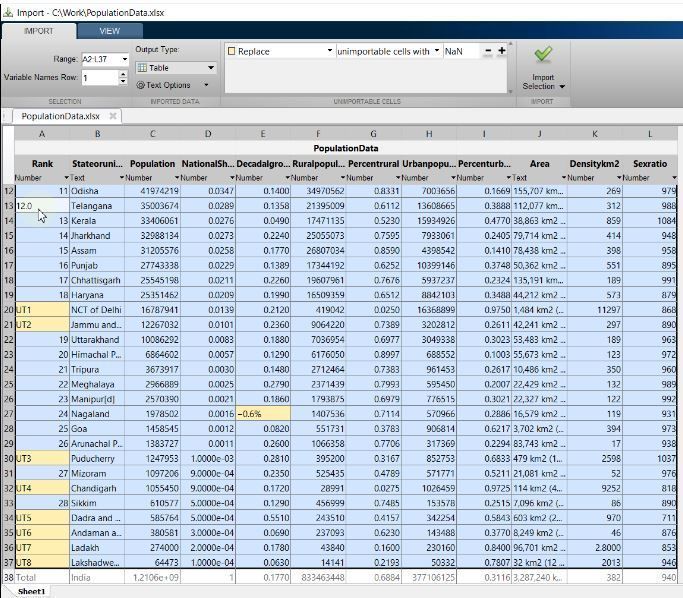

We want to find out States where the female to male sex ratio is less than 90%. It is very easy with MATLAB when we use logical indexing.

Using More than one Condition
Let’s look at one example of compound conditions. I am creating a matrix big_data of hundred rows and hundred columns. Now if we want to find values between 20 and 30 and assign them to a variable. MATLAB creates a new column vector.
>> big_data = randi(100, 100)
>> lessthan30_greaterthan20 = big_data((big_data < 30) & (big_data > 20))
Let’s replace these values with one in the big_data matrix.
>> big_data((big_data < 30) & (big_data > 20)) = 0
Have you used logical indexing or some other techniques? Let me know in the comment section below.
Video Tutorial
Check the video below for quick practical tutorial.